GUEST EDITORS

Syed Ali Abutalib, MD

L. Jeffrey Medeiros, MD
The ASCO Post is pleased to present Hematology Expert Review, an ongoing feature that occasionally quizzes readers on issues in hematology. In this installment, Drs. Abutalib and Medeiros highlight the rare primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) of the central nervous system (CNS). For each quiz question that follows, select the one best answer. The correct answers and accompanying discussions follow.
Question 1
Which of the following statements about primary DLBCL of the CNS is correct?
A. This neoplasm accounts for up to 1% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas.
B. This neoplasm has a female predominance.
C. In the past 2 decades, the incidence of this neoplasm has decreased among patients older than age 60.
D. About 90% of these neoplasms involve the supratentorial region.
Question 2
Which of the following statements about the microscopy of primary DLBCL of the CNS is correct?
A. Neoplastic cells are small in size.
B. Infiltration of cerebral blood vessels is uncommon.
C. Areas of geographic necrosis are common.
D. There is an absence of inflammatory cells.
Question 3
Which of the following statements about immunophenotype for primary DLBCL of the CNS is correct?
A. This neoplasm is positive for PAX5, CD19, CD20, CD22, and CD79a.
B. Most cases express BCL6 and MUM1.
C. CD10 is expressed in the minority of cases.
D. All of the above
Answers to Hematology Expert Review Questions
Question 1
Which of the following statements about primary DLBCL of the CNS is correct?
Correct answer: A. This neoplasm accounts for up to 1% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas.
Expert Perspective
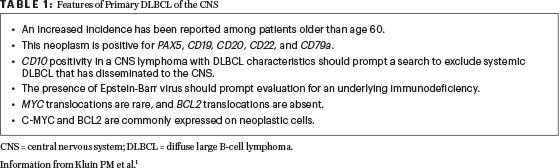
Primary DLBCL of the CNS accounts for up to 1% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas. This lymphoma can affect patients of any age, with a peak incidence in the fifth to seventh decades of life, a median age of 56 years, and a male-to-female ratio of 3:2.1 In the past 2 decades, an increased incidence has been reported among patients aged 60 years and older. About 60% (not 90%) of these neoplasms involve the supratentorial region. Less frequently affected sites include the posterior fossa and the spinal cord.1 (See Table 1 for features of this rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.)
Question 2
Which of the following statements about microscopy of primary DLBCL of the CNS is correct?
Correct answer: C. Areas of geographic necrosis are common.
Expert Perspective
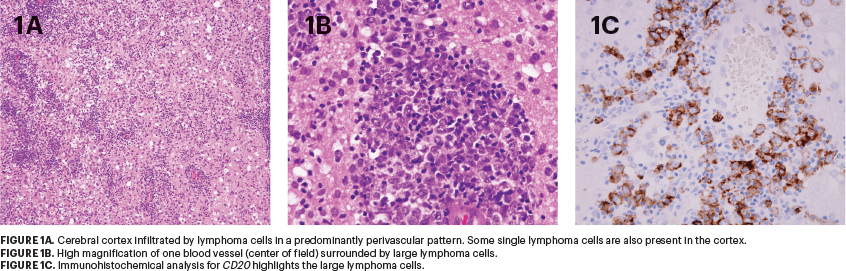
Primary CNS lymphoma is usually highly cellular with diffuse growth patterns. Centrally, large areas of geographic necrosis are common and can complicate the diagnosis. At the periphery, a perivascular infiltration (“cuffing”) pattern is frequently seen (Figures 1A and 1B). Infiltration of cerebral blood vessels causes fragmentation of the argyrophilic fiber network.1 From these perivascular cuffs, tumor cells invade the neural parenchyma. The lymphoma cells are medium to large in size, round, oval, irregular, or pleomorphic nuclei and distinct nucleoli, corresponding to centroblasts or immunoblasts.1
The neoplasm is often accompanied by prominent microglial activation and a reactive inflammatory infiltrate. This infiltrate consists of mature T cells and sometimes also lipid-laden (foamy) histiocytes.
Question 3
Which of the following statements about immunophenotype for primary DLBCL of the CNS is correct?
Correct answer: D. All of the above.
Expert Perspective
The neoplastic cells are mature B cells with an immunophenotype positive for PAX5, CD19, CD20, CD22, and CD79a (Figure 1C). IgM and IgD, but not IgG, are expressed, with either kappa or lambda light chain restriction. Most cases express BCL6 (60%–80%) as well as IRF4/MUM1 (~90%). CD10 positivity is unusual in primary DLBCL of the CNS, and expression of CD10 should prompt a search to exclude systemic DLBCL that has disseminated to the CNS. Most cases (~80%) of primary DLBCL of the CNS are positive for BCL2 and MYC expression.
DISCLOSURE: Dr. Abutalib is an advisor for AstraZeneca. Dr. Medeiros reported no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCE
1. Kluin PM, Deckert M, Ferry JA: Primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the CNS, in Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al (eds.): WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, pp 300-302. Lyon France, International Agency for Research in Cancer, 2017.

